你只需要补丁吗?(convMixer)
这是 PyTorch 对论文《补丁就是你所需要的?》的实现
。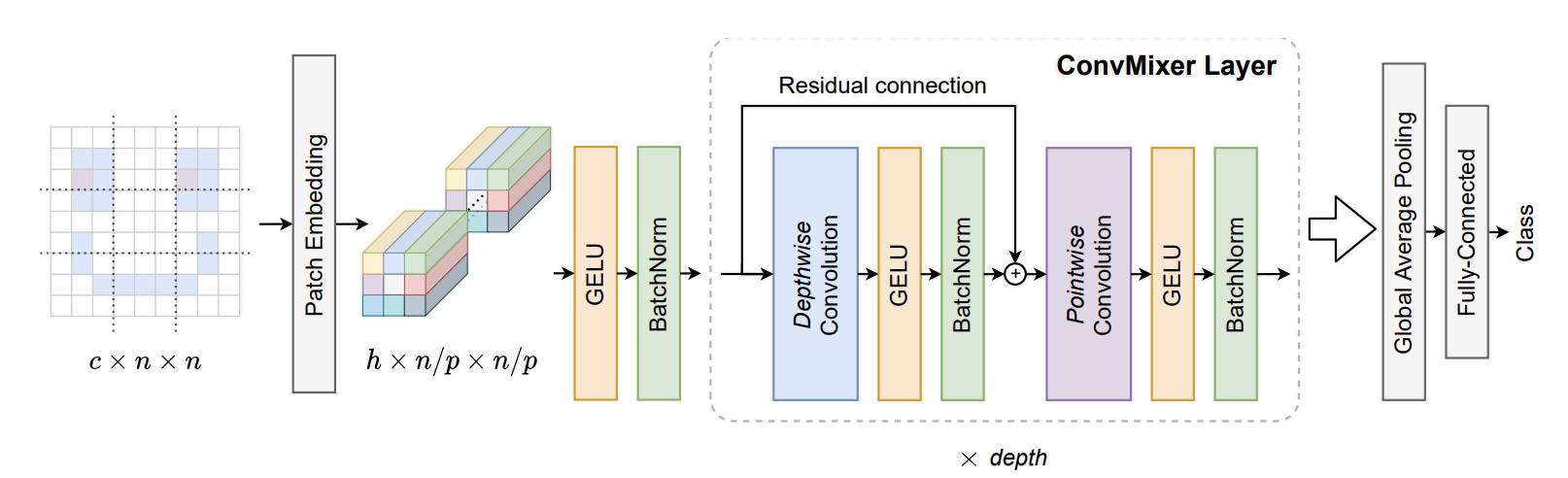
convMixer 类似于 MLP 混音器。MLP-Mixer 通过在空间维度上应用 MLP,然后在信道维度上应用 MLP 来分离空间维度和信道维度的混音(空间 MLP 取代 vIT 注意力,信道 MLP 是 ViT 的 FFN)。
ConvMixer 使用卷积进行通道混合,使用深度卷积进行空间混合。由于它是卷积而不是整个空间的完整的 MLP,因此与 vIT 或 MLP-Mixer 相比,它只混合附近的批次。此外,MLP-Mixer 每次混合使用两层 MLP,ConvMixer 每次混合使用单层。
该论文建议删除信道混合(逐点卷积)上的剩余连接,在空间混合(深度卷积)上仅使用残差连接。他们还使用批量标准化而不是图层标准化。
36import torch
37from torch import nn
38
39from labml_helpers.module import Module
40from labml_nn.utils import clone_module_list43class ConvMixerLayer(Module):d_model是补丁嵌入中的通道数,kernel_size是空间卷积内核的大小,
52 def __init__(self, d_model: int, kernel_size: int):57 super().__init__()深度卷积是每个通道的单独卷积。我们使用卷积层来完成此操作,该卷积层的组数等于通道数。因此,每个频道都是它自己的组。
61 self.depth_wise_conv = nn.Conv2d(d_model, d_model,
62 kernel_size=kernel_size,
63 groups=d_model,
64 padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)深度卷积后激活
66 self.act1 = nn.GELU()深度卷积后的归一化
68 self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(d_model)逐点卷积是一种卷积。即补丁嵌入的线性变换
72 self.point_wise_conv = nn.Conv2d(d_model, d_model, kernel_size=1)逐点卷积后激活
74 self.act2 = nn.GELU()逐点卷积后的归一化
76 self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(d_model)78 def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):对于围绕深度卷积的剩余连接
80 residual = x深度卷积、激活和归一化
83 x = self.depth_wise_conv(x)
84 x = self.act1(x)
85 x = self.norm1(x)添加剩余连接
88 x += residual逐点卷积、激活和归一化
91 x = self.point_wise_conv(x)
92 x = self.act2(x)
93 x = self.norm2(x)96 return x99class PatchEmbeddings(Module):d_model是补丁嵌入中的通道数patch_size是补丁的大小,in_channels是输入图像中的通道数(rgb 为 3)
108 def __init__(self, d_model: int, patch_size: int, in_channels: int):114 super().__init__()我们创建一个卷积层,其内核大小和步长等于补丁大小。这相当于将图像分割成色块并在每个面片上进行线性变换。
119 self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, d_model, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)激活功能
121 self.act = nn.GELU()批量标准化
123 self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(d_model)x是形状的输入图像[batch_size, channels, height, width]
125 def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):应用卷积层
130 x = self.conv(x)激活和规范化
132 x = self.act(x)
133 x = self.norm(x)136 return x139class ClassificationHead(Module):d_model是补丁嵌入中的通道数,n_classes是分类任务中的类数
149 def __init__(self, d_model: int, n_classes: int):154 super().__init__()平均池
156 self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))线性层
158 self.linear = nn.Linear(d_model, n_classes)160 def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):平均汇集
162 x = self.pool(x)得到嵌入,x
会有形状[batch_size, d_model, 1, 1]
164 x = x[:, :, 0, 0]线性层
166 x = self.linear(x)169 return x172class ConvMixer(Module):conv_mixer_layer是单个 C onvMixer 层的副本。我们制作它的副本来制作 ConvMixern_layers。n_layers是 ConvMixer 层(或深度)的数量。patch_emb是补丁嵌入层。classification是分类头。
179 def __init__(self, conv_mixer_layer: ConvMixerLayer, n_layers: int,
180 patch_emb: PatchEmbeddings,
181 classification: ClassificationHead):189 super().__init__()补丁嵌入
191 self.patch_emb = patch_emb分类主管
193 self.classification = classification制作 C onvMixer 图层的副本
195 self.conv_mixer_layers = clone_module_list(conv_mixer_layer, n_layers)x是形状的输入图像[batch_size, channels, height, width]
197 def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):获取补丁嵌入。这给出了形状的张量[batch_size, d_model, height / patch_size, width / patch_size]
。
202 x = self.patch_emb(x)穿过 ConvMixer 图层
205 for layer in self.conv_mixer_layers:
206 x = layer(x)分类头,获取日志
209 x = self.classification(x)212 return x
